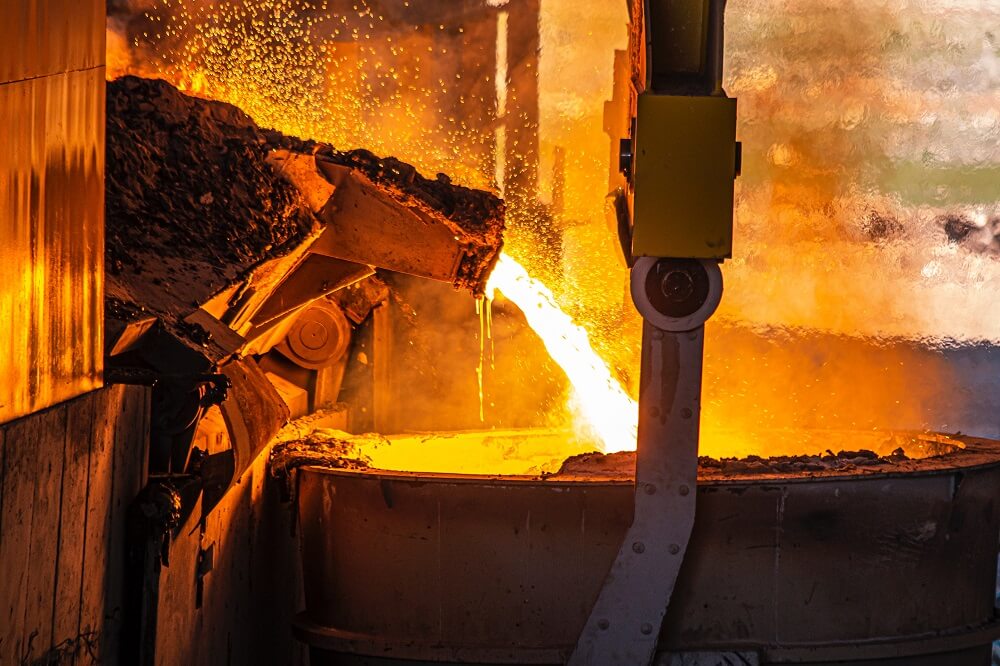
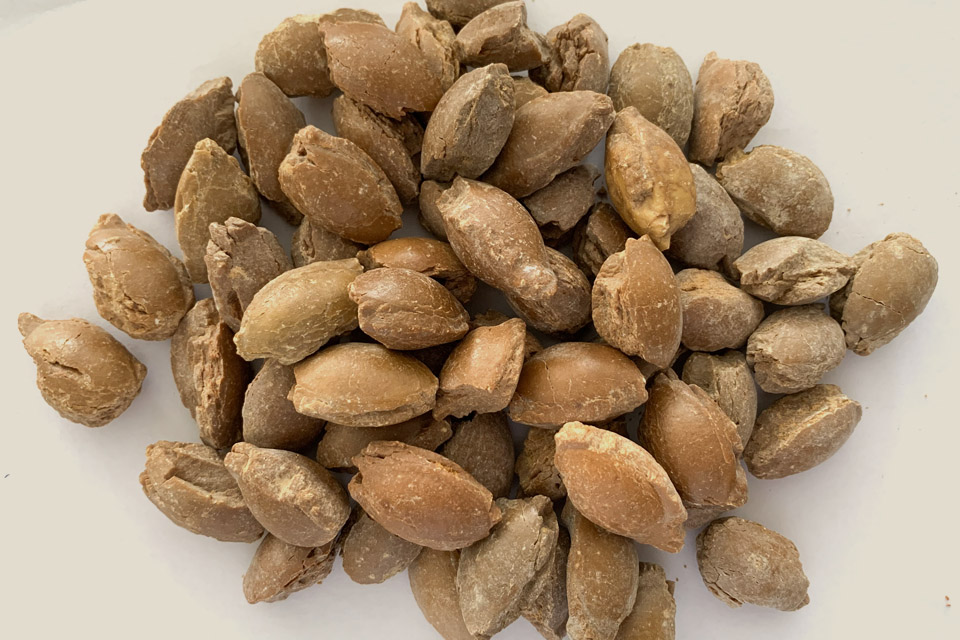
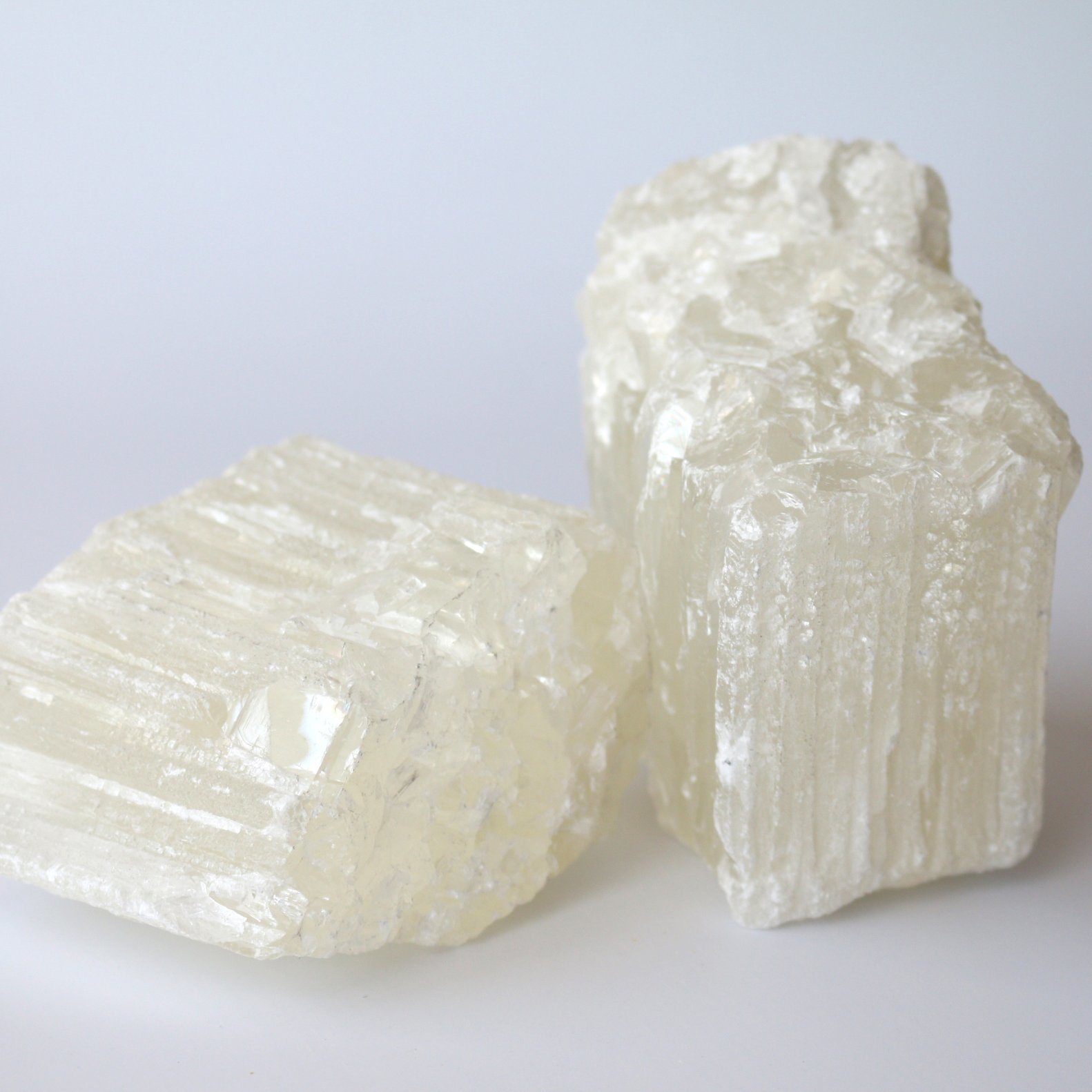
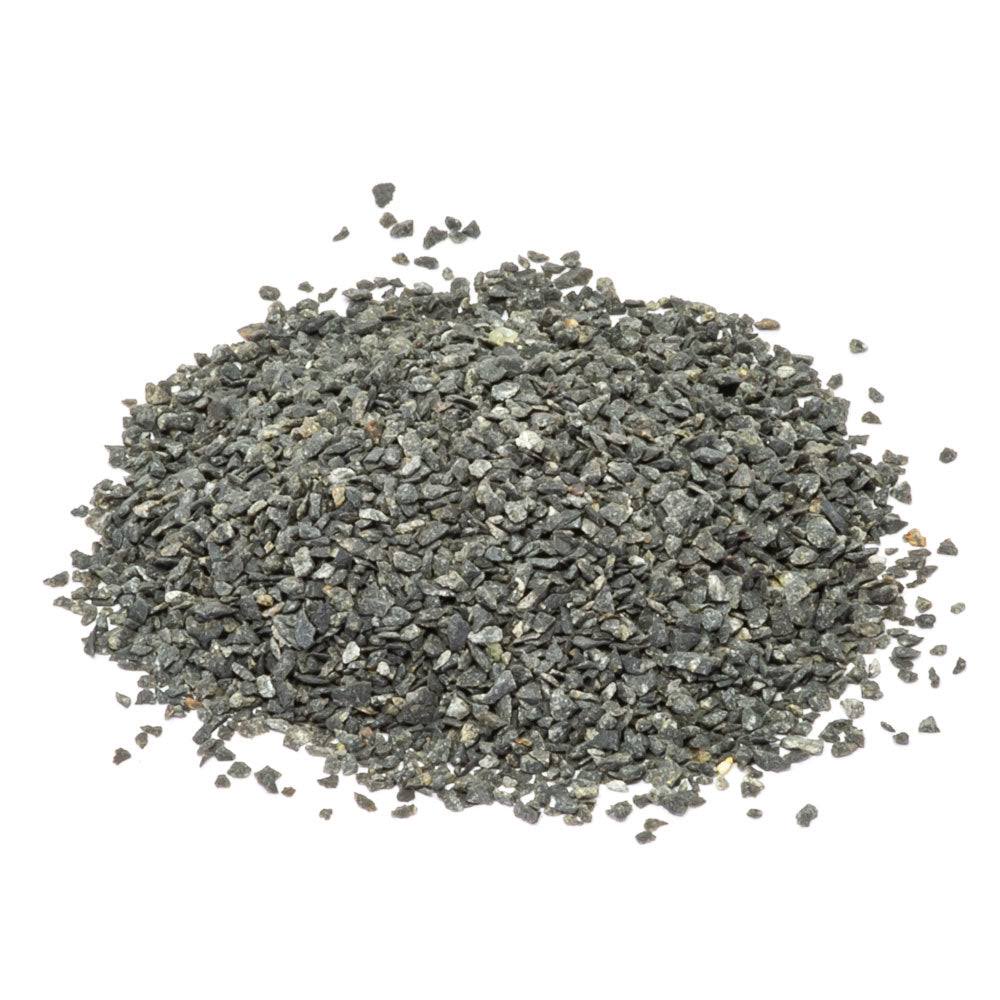
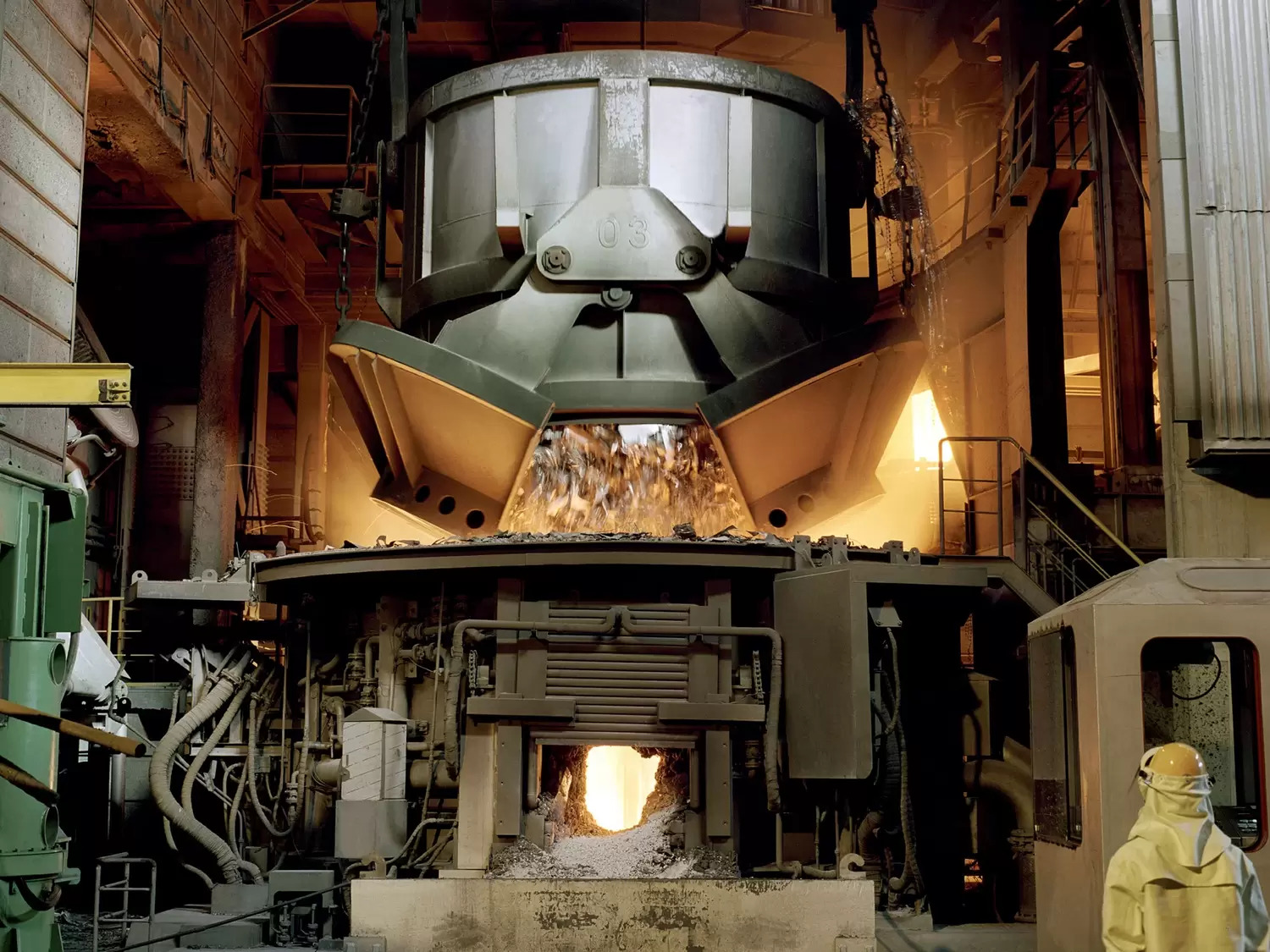
Crucial Components for Electric Arc Furnaces (EAF)
- Home
- Pennekamp Middle East
- Crucial Components for Electric Arc Furnaces (EAF)

At PENNEKAMP Middle East LLC, we are a leading provider of high-quality refractory products for businesses across a wide range of Refractory and Steel industries. With over 25 years of experience in the refractory industry, we have established ourselves as a reliable partner for companies looking for durable and cost-effective refractory solutions.
Raw Materials PDF
Finished Products PDF
Raw Materials PDF
Finished Products PDF